Request an appointment with our dentist today!
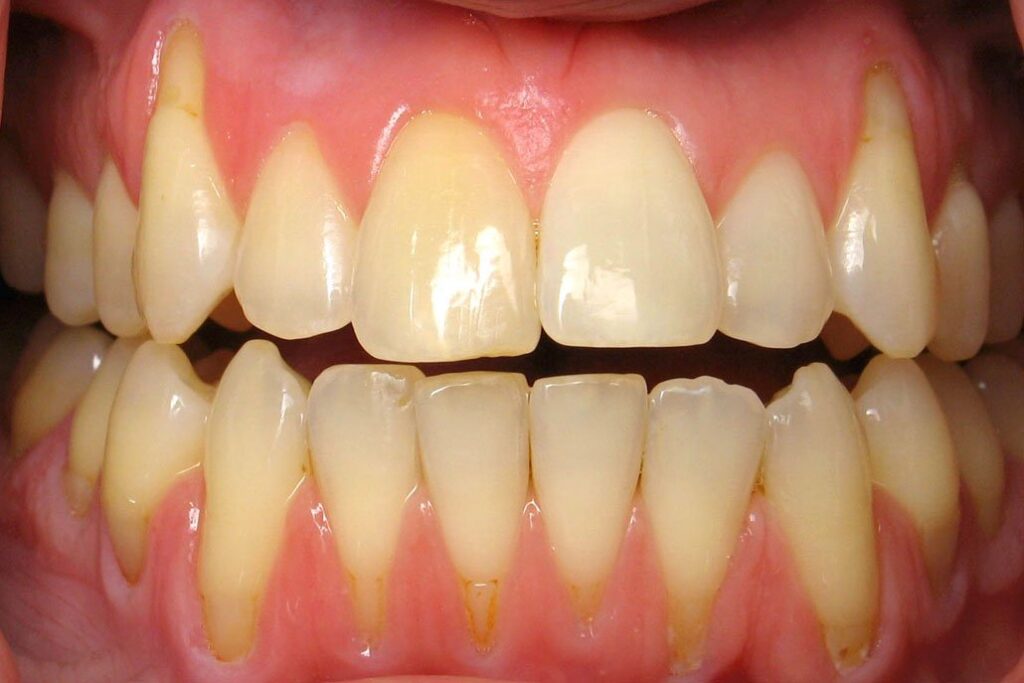
These are bacterial gum infections that destroy gum tissue and supporting bone that hold your teeth in place. Gum disease is the main cause of gum recession.
Some people may be more susceptible to gum disease. In fact, studies show that 30% of the population may be predisposed to gum disease, regardless of how well they care for their teeth.
If you brush your teeth too hard or the wrong way, it can cause the enamel on your teeth to wear away and your gums to recede.
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and rinsing with antibacterial mouthwash makes it easy for plaque to turn into calculus (tartar) -- a hard substance that builds on and between your teeth and can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning. It can lead to gum recession.
Fluctuations in female hormone levels during a woman's lifetime, such as in puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums more sensitive and more vulnerable to gum recession.
Tobacco users are more likely to have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove and can cause gum recession.
Clenching or grinding your teeth can put too much force on the teeth, causing gums to recede.
When teeth do not come together evenly, too much force can be placed on the gums and bone, allowing gums to recede.
Jewelry can rub the gums and irritate them to the point that gum tissue is worn away.
During this procedure, the dentist or periodontist folds back the affected gum tissue, removes the harmful bacteria from the pockets, and then snugly secures the gum tissue in place over the tooth root, thus eliminating the pockets or reducing their size.
If the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed as a result of gum recession, a procedure to regenerate lost bone and tissue may be recommended. As in pocket depth reduction, your dentist will fold back the gum tissue and remove the bacteria. A regenerative material, such as a membrane, graft tissue, or tissue-stimulating protein, will then be applied to encourage your body to naturally regenerate bone and tissue in that area. After the regenerative material is put in place, the gum tissue is secured over the root of the tooth or teeth.
There are several types of gum tissue graft procedures, but the most commonly used one is called a connective tissue graft. In this procedure, a flap of skin is cut at the roof of your mouth (palate) and tissue from under the flap, called subepithelial connective tissue, is removed and then stitched to the gum tissue surrounding the exposed root. After the connective tissue -- the graft -- has been removed from under the flap, the flap is stitched back down.
During another type of graft, tissue is taken directly from the roof of the mouth instead of under the skin. Sometimes, if you have enough gum tissue surrounding the affected teeth, the dentist is able to graft gum from near the tooth and not remove tissue from the palate. This is called a pedicle graft. Your dentist can determine the best type of procedure to use on you based on your individual needs.
Yes, gum recession is quite common, especially as people get older. Many adults have some degree of gum recession. It’s important to keep an eye on your gums and maintain good oral hygiene to prevent it from getting worse.
Gum recession can lead to tooth loss if it’s not treated because it may be a sign of advanced gum disease. When the gums recede, they can’t support the teeth as well, which might make the teeth loose over time.
While natural remedies like oil pulling or using saltwater rinses can help with gum health, they are not cures for gum recession. It’s always best to seek advice from a dental professional for proper treatment.
Sometimes, dental treatments like braces can contribute to gum recession if the teeth move too quickly or if they’re not cared for properly during treatment. Always follow your orthodontist’s instructions for care to minimize risks.
It’s less common for children to have gum recession, but it can happen, usually due to aggressive brushing or poor oral hygiene. It’s important to teach children proper brushing techniques and ensure they have regular dental check-ups.
Ignoring receding gums can lead to more serious dental issues, including severe gum disease, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss. It can also increase the risk of infections and other health problems related to poor oral health.